A Memorandum for Use by Kansas School Boards
In Developing Science Curriculum Regarding Origins Issues
John H. Calvert, Esq.
May 22, 2000
It has been argued that Intelligent Design, although not a religion, may not be science. If it is not science, then perhaps it should be excluded from the science curriculum for Grades K-12 on that ground.
The short answer is that ID is science. For logical, cultural and legal reasons it would be improper for a School District to censor evidence of design from those parts of the curriculum that discuss the cause life and its diversity.
In discussing these issues I will address the following:
| • | What is Intelligent Design? |
| • | Logical Inferences of Design Based on Scientific Observations of Data Occurring in Nature are within the realm of Science. |
| • | Design can not be censored without risking a violation of the Neutrality Required by the Establishment and Speech Clauses of the Constitution. |
| • | Suggestions for Including Design in a School Science Curriculum. |
What is Intelligent Design?
Intelligent Design holds that design is empirically detectable in nature, and particularly in living systems.
What is a “design?” A Design is a Pattern of Events Arranged by Intent.
A design (noun) is nothing more than a pattern of events arranged by intent or design (verb).
An event is an occurrence or a happening. Each of the six letters in the word “Design” reflect a separate event.
Events result from one of three causes: chance, necessity (the operation of physical or chemical laws) or intent/design.
Intent is a state of MIND that directs action towards a particular object.
A MIND is the part of an information processing system that PERCEIVES, THINKS, REASONS AND DECIDES OR FORMS CONCLUSIONS.
 Thus, when a bird builds a nest it does so by processing information with its mind. The sticks and twigs that reflect the many events that make up the nest have not been arranged by any physical or chemical law, but rather by the information processing system that exists in the bird’s head. The same is true for human minds which operate on a far more sophisticated level. Instead of building birds’ nests, we build sky scrapers. Our minds arrange events in patterns which we call designs. This memo reflects a pattern of events arranged by intent.
Thus, when a bird builds a nest it does so by processing information with its mind. The sticks and twigs that reflect the many events that make up the nest have not been arranged by any physical or chemical law, but rather by the information processing system that exists in the bird’s head. The same is true for human minds which operate on a far more sophisticated level. Instead of building birds’ nests, we build sky scrapers. Our minds arrange events in patterns which we call designs. This memo reflects a pattern of events arranged by intent.
What are Causes of other Patterns of Events? Patterns of events not arranged by intent, have been arranged by chance, necessity or a combination of the two.
 Patterns of events can also be arranged by “necessity.” A necessary event is one that is required to happen due to the laws of chemistry and physics. A salt crystal is an example of a pattern of events arranged only by chance and necessity without any direct input from a mind. When, by chance, sodium and chlorine ions are deposited into a body of water with no outlet the positively charged sodium ions will be attracted to the negatively charged chlorine ions to form a very regular three dimensional crystal lattice in the form of a cube. The mineral that is produced is called halite. Sandstones also reflect a pattern of events arranged by necessity. The size of the grains found in the rock will vary with the strength of the current. In this case the pattern reflects the operation of the law of gravity in an aquatic environment.
Patterns of events can also be arranged by “necessity.” A necessary event is one that is required to happen due to the laws of chemistry and physics. A salt crystal is an example of a pattern of events arranged only by chance and necessity without any direct input from a mind. When, by chance, sodium and chlorine ions are deposited into a body of water with no outlet the positively charged sodium ions will be attracted to the negatively charged chlorine ions to form a very regular three dimensional crystal lattice in the form of a cube. The mineral that is produced is called halite. Sandstones also reflect a pattern of events arranged by necessity. The size of the grains found in the rock will vary with the strength of the current. In this case the pattern reflects the operation of the law of gravity in an aquatic environment.
 Events can also occur by chance. A chance event is one that (a) can not be predicted, and (b) is not controlled by intent or necessity/law. We all know what chance events are if we have gone to a casino. Assume I have a bag of 26 scrabble pieces, each of which bears a different letter of the alphabet. What are my chances of spelling the word “DESIGN” by blindly putting my hand in the bag and pulling out the correct letters in the correct sequence (assuming that I put each piece back after I have noted the letter pulled)? The chance of pulling the D is 1/26, the chance of pulling D and E in that sequence is 1/26 x 1/26 or 1/676, etc. Thus the chance of spelling DESIGN in sequence is 1/26×1/26×1/26×1/26×1/26×1/26 = 1 in 308,915,776.
Events can also occur by chance. A chance event is one that (a) can not be predicted, and (b) is not controlled by intent or necessity/law. We all know what chance events are if we have gone to a casino. Assume I have a bag of 26 scrabble pieces, each of which bears a different letter of the alphabet. What are my chances of spelling the word “DESIGN” by blindly putting my hand in the bag and pulling out the correct letters in the correct sequence (assuming that I put each piece back after I have noted the letter pulled)? The chance of pulling the D is 1/26, the chance of pulling D and E in that sequence is 1/26 x 1/26 or 1/676, etc. Thus the chance of spelling DESIGN in sequence is 1/26×1/26×1/26×1/26×1/26×1/26 = 1 in 308,915,776.
Thus, as the complexity of the pattern increases, the probability of its occurrence by chance decreases.
2. Intelligent Design Holds that Design is Empirically Detectable in Nature.
Intelligent Design holds that design is empirically detectable in nature and particularly in living systems. Stated another way, Intelligent Design holds that we can look at a pattern of events and reliably infer from the arrangement of events constituting the pattern and surrounding circumstances whether the events have been arranged by intent through the use of a mind or whether the pattern is more likely the result of only chance and necessity. Thus, Intelligent Design is essentially nothing more than an inference. It is not a philosophy. It is not a religion. It is merely an inference based on observations of patterns of events that occur in nature.
The word “intelligent” in the phrase “intelligent design” is perhaps even superfluous since any design necessarily implies a mind or some form of intelligence as the agent that causes the events to be arranged into a “design.”
Design detection involves three steps.
| • | First: Find a pattern of events that is functional, carries a message or has some discernable structure – that reflects “specified complexity.” |
| • | Second: Rule out Necessity as a cause of the pattern. |
| • | Third: Rule out Chance as a cause of the pattern. |
If you find such a pattern and you conclude that it is not likely that it results from chance or necessity, then you should be able to reasonably infer that the pattern is designed. – i.e, the product of some mind. This method of design detection is outlined in considerable detail by William A. Dembski who holds Ph.Ds. in mathematics and philosophy in the “Design Inference.” (1)
Lets look at the first step – determining whether the pattern reflects “specified complexity. Although this may be an oversimplification of the detailed description in the Design Inference, generally specified complexity exists when the pattern conveys a message, consists of a direction or performs some function that is independent of the function of each of the events that make up the pattern. Specified complexity reflects an ordering of events by intention. Hence, once we do see function, direction or purpose in a form or a pattern of events then we have evidence of intention that supports a design inference.
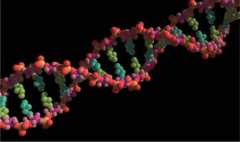 Lets assume that the pattern of events to be analyzed is the sequence of nucleotide bases that appear in the DNA sequence of the first cell. Current science textbooks suggest that this sequence along with the sequence for all of the other genes needed was arranged only by chance and necessity operating on a prebiotic soup containing the necessary chemical constituents. The alternative explanation is that the patterns of events consisting of the DNA together with all the other machinery necessary to the existence of a replicating cell, was arranged by design.
Lets assume that the pattern of events to be analyzed is the sequence of nucleotide bases that appear in the DNA sequence of the first cell. Current science textbooks suggest that this sequence along with the sequence for all of the other genes needed was arranged only by chance and necessity operating on a prebiotic soup containing the necessary chemical constituents. The alternative explanation is that the patterns of events consisting of the DNA together with all the other machinery necessary to the existence of a replicating cell, was arranged by design.
Using design detection, we would consult with biochemists and inquire whether the DNA sequence has structure, function or carries a message. The answer is that the sequence does all three. In fact the sequence reflects a language. This observation is reflected daily in the science literature. The apparent design exhibited by living organisms is reflected by the labels put on cellular systems by modern science:
| • | genetic “code” |
| • | “blueprint” of life |
| • | biological mechanism was “invented” |
| • | biological system uses this “strategy,” |
| • | biological information” |
| • | hardware and software” in the cell |
Perhaps the most famous critic of design is Richard Dawkins who admits that living organisms give the appearance of design:
“Biology is the study of complicated things that give the appearance of having been designed for a purpose.”
[Richard Dawkins, The Blind Watchmaker, at 1 (W.W. Norton & Company, 1996)].
Accordingly, the first step in the design detection process is more or less acknowledged by modern science. No one seriously argues that living systems do not appear to be designed.
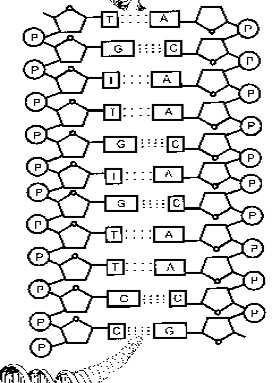 The next step is to rule out necessity (physical and chemical laws) as an explanation for the arrangement of the DNA sequence. Scientists interested in design detection note that there is no known chemical or physical characteristic that requires any particular arrangement of nucleotide bases along the sugar and phosphate backbones of the DNA strand.(2) Since there is no required arrangement, law or necessity does not appear to play a role in the arrangement of the precise instructions which provide the “blueprint” for the formation of the entire living organism. Scientists have also noted that if there was a law that would require a particular arrangement, it would be impossible for the DNA to have the capacity to effectively carry any biological information.(3) The purpose of this discussion is not to prove this point, but merely to show how design detection works and to also note that it involves observations that are guided by the use of physics, chemistry and biochemistry.
The next step is to rule out necessity (physical and chemical laws) as an explanation for the arrangement of the DNA sequence. Scientists interested in design detection note that there is no known chemical or physical characteristic that requires any particular arrangement of nucleotide bases along the sugar and phosphate backbones of the DNA strand.(2) Since there is no required arrangement, law or necessity does not appear to play a role in the arrangement of the precise instructions which provide the “blueprint” for the formation of the entire living organism. Scientists have also noted that if there was a law that would require a particular arrangement, it would be impossible for the DNA to have the capacity to effectively carry any biological information.(3) The purpose of this discussion is not to prove this point, but merely to show how design detection works and to also note that it involves observations that are guided by the use of physics, chemistry and biochemistry.
The final step is to rule out chance as a mechanism for producing a pattern of events which appear to have been arranged by design. Without attempting to get into the detail, the estimates of the probability of a simple DNA sequence coding for a single protein with a 100 amino acids by chance has been set at effectively zero.(4) Recent scientific studies suggest that the first cell is thought to have had DNA that would code for at least 300 proteins, each consisting of 100 or more amino acids.
Ruling out chance thus involves a knowledge and use of statistics, mathematics and probability theory as well as biochemistry. Because probability is affected by the amount of time involved and the number of trials that may be involved, the fossil record comes into play. Darwin postulated that his theory would not work if there were not enough time over which change could be effected gradually in a continuum of numerous small steps. Hence, a design theorist will examine the fossil record to determine the amount of time that exists between changes in the development of diversity. Sharp bursts of development with intervening periods of biological stasis support design theory, while gradualism tends to support chance based mechanisms.
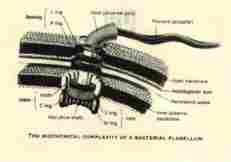 Chance explanations also are vulnerable to observations relating to the nature of complexity itself. Biochemist Michael Behe has demonstrated that biological mechanisms in living organisms are irreducibly complex. He uses as an example a bacterial flagellum that requires 40 moving parts. This biological machine that is believed to be a component of the most primitive cell will not work at all unless all of the parts are assembled at the same time. Natural selection can not build such a machine because the individual parts have no selective value in isolation. They have selective value only when they become a part of a functional whole.(5) The conclusion that one draws from this observation is apparent when one considers the efficacy of a mechanism that operates on chance and necessity alone. It operates merely like a sieve. Because it does not have the tools that a mind has to perceive, think, decide and to direct the arrangement and coordination of future events, it is a mechanism whose competency for assembly is questionable in concept alone.
Chance explanations also are vulnerable to observations relating to the nature of complexity itself. Biochemist Michael Behe has demonstrated that biological mechanisms in living organisms are irreducibly complex. He uses as an example a bacterial flagellum that requires 40 moving parts. This biological machine that is believed to be a component of the most primitive cell will not work at all unless all of the parts are assembled at the same time. Natural selection can not build such a machine because the individual parts have no selective value in isolation. They have selective value only when they become a part of a functional whole.(5) The conclusion that one draws from this observation is apparent when one considers the efficacy of a mechanism that operates on chance and necessity alone. It operates merely like a sieve. Because it does not have the tools that a mind has to perceive, think, decide and to direct the arrangement and coordination of future events, it is a mechanism whose competency for assembly is questionable in concept alone.
3. Design detection is not a new science. It is used in a number of other disciplines.
| • | Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence where scientists examine sound waves from outer space to determine patterns of events arranged by intent rather than by chance or necessity. |
| • | Forensic Sciences where scientists examine patterns of events surrounding death to determine whether the patterns were arranged by intent (i.e. murder) or by chance or necessity. It is also extensively used in arson investigations to determine whether fires have resulted by accident or by design. |
| • | Cryptanalysis where scientists examine patterns of characters to determine whether they convey a message or whether the characters merely reflect random sequences. |
| • | Archaeology where scientists examine artifacts to determine whether they were fashioned by intent or by chance and necessity as in the case of stone and markings on the walls of caves and stones. |
| • | Copyright infringement, Plagiarism and Musicology where scientists examine patterns of events in writings to determine whether they have been copied from another work by design. |
| • | Reverse engineering where scientists examine the structure of living systems to determine why the system might have been designed to have the particular structure so as to better understand how the system works. William Harvey used design theory to hypothesize blood circulation in the human body. |
In summary design detection involves the observation of things which occur in nature using accepted scientific knowledge and methodologies.
The Implications of Design and Naturalistic Mechanisms of Chance and Necessity Conflict
Although design necessarily implies a mind, an inference of design does not require any particular type or kind of mind. A bird’s nest is designed by a natural mind yet we do not infer from the nest a “God” or supernatural being as the direct builder of the nest. The same is true of inventions of human minds. At the present rate at which technology is progressing one could reasonably hypothesize that some day humans will be able to create living organisms from scratch. They presently build computers that can play chess and perform other amazing feats of information processing. Although humans have minds, we do not infer from their designs that the designs are the product of a God. In using the word “God” I refer to the definition in the dictionary of a “ruler of the world and its creation – one who presently controls nature and the universe.”
Thus, inferring that life is designed does not necessarily require an inference that the designer is a “God.” Of course one could choose to believe that based on the data, but such a belief is not required. The designer or designers could consist of a mind or minds from another civilization that inhabit another galaxy. We do not know and the Intelligent Design movement does not speculate on who the designer is or was. ID merely contends that the patterns of events under examination are more likely to have been produced by a mind than by only a mechanism of chance and necessity such as Neo Darwinism.
Although design inferences do not entail a God, it is acknowledged that they provide a logical basis for that belief. Accordingly, design inferences do support theistic beliefs.
On the other hand, explanations that life and its diversity result only from chance and necessity and that Design or a mind is not involved do generate the exact opposite and competing belief. Neo Darwinian explanations that life does not result from any direct action from any mind suggest that no God is responsible for life or its diversify. This is directly inconsistent with most theistic beliefs that God created the universe and the life in it and presently continues to control that creation.
Thus, evidence of design generates a basis for theistic beliefs while naturalistic mechanisms generate a basis for atheistic beliefs.
-
- Logical Inferences of Design Based on Scientific Observations of Data Occurring In Nature Are within the Realm of “Science.”
- To be Consistent with State Science Standards, School Boards Must Define Science by Logic rather than by Naturalistic Limitations.
- Naturalistic Definitions of Science which exclude design are improper and are not Required by Law.
Opponents of design theory argue that design is not scientific because it does not explain by resort to “natural law.” Natural law means the laws of chemistry and physics. According to this definition, anything not fully explainable by the laws of chemistry and physics is outside the realm of science. This definition of science necessarily requires that science be governed by the philosophy of naturalism.
Webster’s Third New International Dictionary defines Naturalism as:
“the doctrine that cause-and-effect laws (as of physics and chemistry) are adequate to account for all phenomena and that teleological [design] conceptions of nature are invalid .”
Naturalism is a philosophy and not science.(6) There is no empirical evidence or data to support the claims of Naturalism that only chance and necessity are responsible for everything and that design inferences are invalid. As indicated by the definition, it is a “doctrine.” The synonym for doctrine is belief. This is consistent with the Random House definition of Naturalism which describes it as a “belief.”
A principal problem with a scientific conclusion that is driven by philosophy rather than by logic is that it has no evidentiary or logical credibility. Scientific conclusions that are dependent only on evidence that exists within certain predescribed boundaries and not on evidence which falls within the excluded range prejudge the issue. Under a naturalistic definition of science, evidence of design is obviously excluded. The exclusion results not from the quality of its evidence, but rather from a philosophical viewpoint. Because design as a cause is excluded, the evidence of design that exists in nature is ignored. The result is that any scientific conclusion about the efficacy of Neo Darwinism as an explanation of life can not have any logical credibility. The philosophy also dictates that alternatives will not be considered.
Although this philosophical exclusion may not make much difference in basic research on issues not involving origins, it is critical when origins issues are addressed. There are only two possible answers to the question of what causes life and its diversity. It is either designed or it is caused only by chance and necessity. If you rule out design, a priori, then you answer the question before it is even asked. The question is prejudged. Because it is prejudged, the answer completely lacks credibility. A credible answer is only one that is allowed to be tested. The only test for a naturalistic explanation is a test of design. If we can not apply that test, then naturalistic explanations for the origin of life can never be scientifically credible.
Although the science texts and the biological community of scientists which have embraced Neo Darwinism openly advocate a naturalistic definition of science, many scientists disagree.(7) Furthermore, there is no law or rule that mandates the use of a naturalistic definition of science when approaching the issue of what causes life and its diversity.
To be Consistent with the State Science Standards, Science Must
be defined by Logic and not by the philosophy of Naturalism.
Perhaps the most significant provision contained in the new science standards is the definition of science. Under the new standards that were adopted by the State Board on December 9, 1999, science is defined as:
“Science is the human activity of seeking logical explanations for what we observe in the world around us. Science does so through the use of observation, experimentation, and logical argument while maintaining strict empirical standards and healthy skepticism.”
The standards that had been proposed by the Science Writing Committee urged that science be driven by naturalism instead of logic. Under those standards the word “natural” was used instead of the word “logical.” By changing “natural”to “logical” the Board directed that science be driven by logic rather than by philosophy. To be consistent with Kansas Science Standards, the Kansas school boards must approach the issue of how we should teach science concerning the origins and diversity of life on a logical rather than a philosophical basis. This being the case, there is no legal reason for excluding design from discussion in science classes either as a critique of Neo Darwinism and its mechanisms of chance and necessity or as an alternative theory of origins.
The Supreme Court definition of Science Does Not Permit the Exclusion of evidence of design and is consistent with the
Definition of Science Contained in the New Science Standards.
In Daubert v. Merrill Dow Corporation, Pharmaceuticals, Inc., 509 U.S. 579 (1993) the Supreme Court squarely addressed the question of what is “science.” In Daubert, Merrill Dow was being sued by two children with serious birth defects alleged to be caused by Benedectin, a drug marketed by Merrill Dow. Merrill Dow produced expert testimony based on a review of extensive scientific literature on the subject that the drug could not have caused the birth defects. The attorney for the children submitted the testimony of eight other well-credentialed experts, who based their conclusion that Benedectin can cause birth defects on animal studies, chemical structure analyses, and the unpublished “reanalysis” of previously published human statistical studies. However, the lower court ruled that the evidence was not admissible because the evidence did not meet the applicable “general acceptance” standard for the admission of expert testimony. It then dismissed the case and the Court of Appeals affirmed, citing Frye v. United States, 54 App. D.C. 46, 47, 293 F. 1013, 1014, for the rule that expert opinion based on a scientific technique is inadmissible unless the technique is “generally accepted” as reliable in the relevant scientific community.
The Supreme Court overruled both courts and sent the case back to the trial court for reconsideration of the evidence presented by the children. In doing so it provided an extensive analysis of how courts should determine whether a proposed scientific view is one that should be heard by a trier of fact. Although Daubert strictly deals with the evidentiary requirements of the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure relating to the admissibility of expert testimony, the principles it announced are consistent with the issue of whether inferences of design from data that occurs in nature are “scientific.”
In overruling Fry, the court in Daubert and in a subsequent ruling(8) established the principles listed below relating to the definition of science.
-
- The definition of science must be flexible to fit the circumstances of
each case. - The definition used should focus on establishing the evidentiary reliability of
the testimony. - In determining evidentiary reliability the focus should be on
whether the testimony’s underlying reasoning or methodology is
scientifically valid and properly can be applied to the facts at issue. - “The inquiry is a flexible one, and its focus must be solely on
principles and methodology, not on the conclusions that they
generate.”
- The definition of science must be flexible to fit the circumstances of
I have included after each principle a discussion as to why design theory meets the criteria.
- The definition of science must be flexible to fit the circumstances of each case.
This principal is particularly applicable to origins science. In origins science, we attempt to explain historical events that can not be directly observed. For example, Neo Darwinism rests on the principle of “biological continuity”- that there is a continuous series of biological ancestors linking each of the present species back to the earliest cell 3.8 billion years ago. Due to the inadequacy of the fossil record and the remoteness of the events, this principle can not be absolutely tested or falsified. Until we find a mind responsible for the apparent design that exists in nature, the theory that the complexity was produced by a mind also can not be absolutely tested or falsified. Accordingly, any definition of science that explores the origins of life and its diversity, must by virtue of the boundaries of our knowledge, be limited to inferences from data that is available and by testing that can be performed on the methods used to reach the inferences. Both design and Neo Darwinism satisfy this definition since the data and methods used to reach their conclusions can be tested.
- The definition used should focus on establishing the evidentiary
reliability of the testimony.
This factor squarely supports the definition of science used in the Kansas Science Education Standards and ID theory. The focus of design detection is to study the evidence or data which exists in nature and to then draw inferences that are the most logical and reliable. Neo Darwinism, however, rejects that approach since it ignores evidence of design for philosophical reasons. Neo Darwinism is not focused on evidentiary reliability because its naturalistic underpinning will not allow that theory to be tested by the evidence of design.
- In determining evidentiary reliability the focus should be on
whether the testimony’s underlying reasoning or methodology is
scientifically valid and properly can be applied to the facts at issue.
Again, design detection relies on essentially the same sorts of reasoning and methodology used in a variety of scientific disciplines. It uses information theory, chemistry, physics, biochemistry, mathematics, statistics, geology, astronomy, cosmology, etc. The underlying data which form the basis for design inferences are seldom in dispute and are generally consistent with and rely upon data that is commonly accepted in the scientific community.
- “The inquiry is a flexible one, and its focus must be solely on
principles and methodology, not on the conclusions that they
generate.”
This principle of the Daubert test is wholly inconsistent with any definition of origins science which philosophically rules out design explanations. In this respect Daubert stands for the proposition that science should be more concerned with getting to the truth rather than in attempting to prove a particular conclusion. This is the primary difficulty with the modern science attempt to ignore and censor evidence of design. It prejudges the issue of what causes life and its diversity. Daubert holds that this is not scientific. Obviously, design theory, which focuses only on the evidence and which rules out no possible explanation on any philosophical basis, satisfies this criteria, while naturalistic approaches to the question do not.
Daubert finally provides that in undertaking an analysis of whether a matter is “scientific,” one should consider those factors which “bear on the inquiry.” Among the factors which the court discussed are those that are listed below. In discussing these factors the court did not rule that the list was all inclusive or that all factors must be present for a theory to be “scientific” but rather indicated that these should be considered in reaching that conclusion.
| • | the theory or technique in question be (and has been) tested? |
As previously mentioned, the underlying design detection techniques and methods can be and have been tested. On the other hand, Neo Darwinism arguably fails this test since its naturalistic underpinning has not permitted its theory to be tested by the evidence of design.
| • | the theory been subjected to peer review and publication? |
Design as a theory of origins has been the subject of discussion since at least the fifth century BC when Aristotle, Plato and Socrates argued that nature was the product of design. The advent of Darwinism and natural selection as a conceptual answer to the diversity of life has provided the basis for modern Science to philosophically rule out design and its supernatural implications.(9) For the most part the criticism of design has not been on the basis of the adequacy or inadequacy of the evidence. Instead, the evidence has been consciously ignored by the scientific community for philosophical reasons. Due to this philosophical exclusion modern science journals will not carry articles regarding intelligent design. However, during the past 20 years a number of books and articles concerning design have been published and reviewed. These books and articles have received a substantial amount of national and professional attention and no substantive criticism has surfaced. Daubert, specifically recognized that when a theory has not had an opportunity to gain wide acceptance, then the weight of this factor should be discounted appropriately in determining whether a subject legitimately falls within the realm of science. Given the long history of design, the extent of current publications about it, our relatively recent ability to examine the complexity of living organisms and their information rich characteristics and the extent of the organized censorship of design, design clearly satisfies this criterion.
| • | the theory attracted widespread acceptance within a RELEVANT scientific community? |
Design theory has obviously not attracted widespread acceptance within the community of modern science which philosophically excludes it from objective consideration. However, it has attracted significant growing acceptance within an open minded community. This has been fueled by our increased understanding of the complexity of living organisms and the fact that they appear to be nothing less than extremely sophisticated information processing systems, all of which require some sort of mind for operation. Information in its generally accepted sense can only be produced by a mind. Chance and necessity operating alone simply do not appear to have the tools necessary to process information. Certainly design does have widespread acceptance within the community of scientists that do not philosophically exclude design as a possible cause of life and its diversity.
| • | the facts and data “of the type reasonably relied upon by experts in the field?” |
As previously stated, design detection relies on the kind of facts and data that are of the type reasonably relied upon by the scientific community.
I believe that the most convincing argument for the scientific nature of design theory is that it is a theory, which because of its nature, can only be properly investigated and analyzed by scientists. Only professionals qualified to practice in the areas of information theory, chemistry, physics, biochemistry, mathematics, statistics, geology, astronomy, cosmology have the competence to thoroughly examine the evidence of design that exists in nature. Accordingly, if design is ruled “unscientific” so that scientists can not legitimately and objectively consider the evidence, a credible answer to the question of what causes life and its diversity will never be forthcoming.
From the above one must conclude that design theory, which focuses on a no holds barred examination of the evidence, is at least as “scientific” as the competing viewpoint, if not more so.
In 1999 the Daubert principles were reaffirmed by the Court in a case dealing with expert testimony on technical rather than scientific testimony [Kumho Tire Co., Ltd., Et al. V. Carmichael Et al. 119 S.Ct. 1167 (1999)].
The effect of Daubert is to supersede the strict demarcation tests applied by Judge Overton in the District Court case of McLean v. Arkansas Board of Education, 529 F.Supp 1255 (E.D. Ark 1982)]. In that case, the Arkansas district court found that a statute that mandated the teaching of “creation science” was unconstitutional. As defined in the statute, “creation science” included a number of tenets relating to the age of the earth, a world wide flood and similar matters found in the first eleven chapters of Genesis. The Court found that this definition was, in effect, a restatement of those provisions of Genesis. An inference that design exists in nature is not “creation science.” Accordingly, on the facts alone, McLean is not pertinent to this discussion. However, the McLean Court did address the question of what constitutes science. In doing so, the Court indicated that science must explain by resort to natural law. Although this may work in some areas of science, it obviously does not work when addressing the issue of what causes life and its diversity if you define “natural law” as only involving chance and necessity.(10) If so, you violate the Daubert principle that conclusions should not drive the inquiry, rather the evidence should drive the inquiry. The McLean definition is also inapplicable in Kansas where science is defined as the activity of seeking “logical” rather than “natural” explanations of what we see in the world around us.
For the foregoing reasons, the School District should not exclude teaching the design alternative to the question of what causes life and its diversity on the grounds that it is not “scientific.”
III. Design can not be censored without violating the Neutrality Required by the Establishment and Speech clauses of the Constitution.
The First Amendment to the Constitution, provides that the federal government will impose no law or regulation “respecting an establishment of religion or prohibiting the free exercise thereof.” The court has also held that by virtue of the 14th Amendment, the First Amendment also applies to any state or local government or subdivision thereof. This has been construed by the Supreme Court to mean that the “principal or primary effect” of a state action must be one that neither advances nor inhibits religion [Board of Education v. Allen, 392 U.S. 236, 243, 88 S.Ct. 1923, 1926 (1968)]. Similarly, the Supreme Court has held that a state institution that encourages open discourse on a subject may not censor single or multiple viewpoints without violating the Free Speech clause of the constitution [Rosenberger v. Rector and Visitors of the University of Virginia, 515 U.S. 819, 831-2, 115 S.Ct. 2510,2518 (1995)].
The neutrality required by the Constitution is articulated by Justice O’Connor in her concurring opinion in the Rosenberg v. Rector, et. al, at page 846 (2525 S.Ct.) as follows:
“‘We have time and again held that the government generally may not treat people differently based on the God or gods they worship, or do not worship.’ [Citations omitted]. This insistence on government neutrality toward religion explains why we have held that schools may not discriminate against religious groups by denying them equal access to facilities that the schools make available to all. [citations omitted]. Withholding access would leave an impermissible perception that religious activities are disfavored: ‘[The message is one of neutrality rather than endorsement; if a State refused to let religious groups use facilities open to others, then it would demonstrate not neutrality but hostility toward religion.’ [citations omitted]. ‘The Religion Clauses prohibit the government from favoring religion, but they provide no warrant for discriminating against religion.'[citations omitted]. Neutrality, in both form and effect, is one hallmark of the Establishment Clause.” (emphasis added)
Although neither design nor Neodarwinism(11) in and of themselves constitute a religion, design and the naturalistic underpinning of Neodarwinism give rise to serious religious implications. As mentioned, although design does not require theism, all theistic religions require design. By excluding design as a possible cause of life and its diversify, naturalism is necessarily hostile to theistic beliefs.
Accordingly, if a public school system censors evidence of design that exists in nature due to the naturalistic philosophy of science it will have the “effect” of inhibiting the religious beliefs of students who are taught to believe that a designer is responsible for life. Under these circumstances, the parent of such a child would have cause to complain that the School was violating the principle of government neutrality. The parents and child would claim an inhibition of their religious beliefs through an organized suppression of evidence consistent with and supportive of those beliefs while having the effect of promoting a philosophy of naturalism that is inconsistent with those beliefs.
By the same token, if a school were to censor naturalistic views of origins, the school system would be denigrating atheistic beliefs while promoting theistic beliefs. In that case, atheistic parents would have cause to complain.
Since the Kansas Standards rule out naturalism and rule in logic, a Kansas School District has no rational basis for excluding design as a causal explanation for life and its diversity. Accordingly, the only way a Kansas school system can achieve the neutrality required by the Supreme Court is to not censor reliable scientific evidence which supports either causal explanation. In this way the evidence of both theories of origins will be allowed to compete freely and to be open to no-holds-barred testing.
- Suggestions for Including Design in a School Science Curriculum.
Consistent with these remarks I would suggest that boards of education consider the following in implementing the new science standards which specifically permit logical explanations of what we see in the world around us:
| • | teachers that they may discuss evidence of design when the issue of the origin of life or its diversify is addressed in science class. Adopt an appropriate statement so that science teachers will know that they will not be discriminated against if they see fit to discuss design in school science classes. A form of suggested statement is attached as Appendix A. |
| • | appropriate texts as a resource such as Of Pandas and People. |
| • | to encourage the development of additional curricula that teachers may suggest as they begin to have actual experience in addressing this viewpoint regarding origins. |
Intelligent Design network, inc.
John H. Calvert, J.D.
Managing Director
-
- The Design Inference, p.36-66 (Cambridge University Press, 1998).
- Stephen C. Meyer, “Word Games, DNA, Design & Intelligence,” p. 48 (Touchstone, July/August 1999).
- Nancy R. Pearcey and Charles B. Thaxton, The Soul of Science, p. 238 (Crossway Books, Wheaton Ill, 1994)
- Consider the DNA sequence for just one gene that codes for a single protein containing 100 amino acids. The probability of the random formation of this sequence has been calculated to be around 4.9 x 10 – 191. This is a mathematical impossibility [Walter L. Bradley and Charles B Thaxton, “Information and the Origin of Life” in the “Creation Hypothesis, ed. J.P. Moreland (Downers Grove, Il.; InterVarsity Press, 1994), p.190. A number of similar probability calculations by a number of scientists have been collected by Dean L. Overman in “A Case Against Accident and Self Organization” at 58 – 65 (Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Inc., 1997)].
- Michael J. Behe, Darwin’s Black Box – The Biochemical Challenge to Evolution, p. 69-73 (The Free Press, 1996).
- Scientists will argue that they are guided by “methodological naturalism” rather than “philosophical naturalism.” However, the distinction is without a difference since there is no practical difference between the effect of the two in application.
- Stephen c. Meyer, The Methodological Equivalence of Design & Descent: Can There Be a Scientific “Theory of Creation”?, at 67 in “The Creation Hypothesis,” ed. by J.P. Moreland (InterVaristy Press, 1994); David K. DeWolf, Stephen C. Meyer and Mark E. DeForrest, “Intelligent Design In Public School Science Curricula,” at 11 (Foundation for Thought and Ethics, 1999)].
- Kumho Tire Co., Ltd., Et al. V. Carmichael Et al. 119 S.Ct. 1167 (1999).
- William A.Dembski, Intelligent Design – The Bridge Between Science and Theology, beginning at 123 (InterVarsity Press, Downers Grove, Ill. (1999).
- A number of noted philosophers have since criticised the definition adopted by the McLean court as essentially being unworkable. See Note 7 and David K. DeWolf, Stephen C. Meyer and Mark E. DeForrest, “Intelligent Design In Public School Science Curricula,” at 11-15 (Foundation for Thought and Ethics, 1999)].
- Although naturalism may not be a “religion,” the highly regarded philosopher and evolutionist Michael Ruse, admits that “evolution” has become a religion [“How evolution became a religion,” http://www.nationalpost.com, (May 13, 2000)]. In that article Ruse states:
“Dr Ruse,” Mr. Gish said, “the trouble with you evolutionists is that you just don’t play fair. You want to stop us religious people from teaching our views in schools. But you evolutionists are just as religious in your way. Christianity tells us where we came from, where we’re going, and what we should do on the way. I defy you to show any difference with evolution. It tells you where you came from, where you are going, and what you should do on the way. You evolutionists have your God, and his name is Charles Darwin.”
“At the time I rather pooh-poohed what Mr. Gish said, but I found myself thinking about his words on the flight back home. And I have been thinking about them ever since. Indeed, they have guided much of my research for the past twenty years. Heretical though it may be to say this — and many of my scientist friends would be only too happy to chain me to the stake and to light the faggots piled around —I now think the Creationists like Mr. Gish are absolutely right in their complaint.
“Evolution is promoted by its practitioners as more than mere science. Evolution is promulgated as an ideology, a secular religion — a full-fledged alternative to Christianity, with meaning and morality. I am an ardent evolutionist and an ex Christian, but I must admit that in this one complaint — and Mr. Gish is but one of many to make it — the literalists are absolutely right. Evolution is a religion. This was true of evolution in the beginning, and it is true of evolution still today.” (emphasis added)
Appendix A
CURRICULUM STATEMENT RELATIVE TO TEACHINGS
ABOUT ORIGINS IN SCIENCE CLASSES
Any teaching about the cause of life and its diversity has religious and philosophical implications. A teaching that life and its diversity results only from mechanisms of chance and necessity, such as evolution guided by random mutation and natural selection, implies that no intelligent agent or god has intervened in the process. Accordingly, the implications of that teaching are consistent with atheism and inconsistent with theistic religions founded on the belief that a God does intervene in the material world. A teaching that life and its diversity may result from design implies the intervention of an intelligent agent. Accordingly, the implications of that teaching are consistent with theism.
Good science education about origins issues should not censor the teaching of evidence of any of the possible causes of life and its diversity so long as the evidence has evidentiary reliability, is relevant to and logically supportive of the issue and is not being presented to advocate any particular religious or philosophical belief. In particular, scientific teachings about the cause of life and its diversity should not be based on a philosophy of naturalism nor should they be based on any religious belief or teaching about creation. Naturalism is “the doctrine that cause-and-effect laws (as of physics and chemistry) are adequate to account for all phenomena and that teleological [design] conceptions of nature are invalid” (Webster’s Third New International Dictionary).
If a teacher is censored from discussing evidence of design so that the teacher may only teach a theory based on mechanisms of chance and necessity, then the school may be causing the state to promote atheistic beliefs in a way that has the effect of denigrating theistic beliefs. If a teacher is censored from discussing evidence of evolution based on natural selection and random mutation so that the teacher may only teach a theory based on design, then the school may be causing the state to promote theistic beliefs in a way that has the effect of denigrating atheistic beliefs and religions which are not theistic.
Teachers should also not be censored from teaching evidence that tends to criticize any theory of origins for the same reasons. Censorship of evidence critical of any theory of origins will tend to promote the protected theory and its atheistic or theistic implications. Censorship of the evidence will also undercut the credibility of the protected theory and will be inconsistent with the fundamental principle of science that all theories should be held open to testing and criticism.
Any conclusions expressed by a teacher regarding the weight of the evidence supporting any particular theory should be formed objectively and tentatively, based on the strength of the evidence and not on any religious or philosophical view or belief. The tentativeness of any such conclusion is important since ultimate answers to the issue of the origin of life are currently unknowable based on available technology.
Teachers should also be encouraged to explain to science students an objective history of the philosophy of science and how that philosophy changed with the advent of Darwinism to a philosophy of naturalism. Science teachers should carefully explain that naturalism is merely a belief or philosophy and that explanations of origins may be affected by this belief or philosophy.

